The Bow Tie Model and Dropped Objects: Risk Management’s Comprehensive Approach
The bow tie model serves as a pivotal tool in risk management, offering insights into managing specific risks. In the industrial context of dropped objects, this model provides a holistic perspective on potential causes, preventive actions, and resulting consequences.
Understanding the DROPS Bow Tie Structure
At its core, the bow tie model mirrors its namesake. The central knot symbolizes the undesired event or hazard – here, a dropped object incident. Causes or threats leading to this event populate the left side, while the right side showcases potential consequences. Barriers or controls bridge these elements, acting as preventive or mitigative measures.
Identifying Causes
Various factors contribute to dropped objects. Human errors, such as mishandling equipment, rank high. Technical failures, like corrosion or material fatigue, also play a part. Additionally, environmental elements, like strong winds or vibrations, pose threats. Each cause potentially triggers the central undesired event.
Implementing Preventive Barriers
Preventive barriers stand between the causes and the event. These proactive measures aim to halt the undesired event. Regular equipment inspections, proper drops training for workers, tethering tools, and standard operating procedures for equipment handling form these barriers.
Assessing Potential Consequences
Dropped object incidents can lead to varied outcomes. These range from minor equipment damage to severe injuries or fatalities. Indirect consequences might include operational downtime, financial setbacks, or company reputational damage.
Mitigating Consequences with Barriers
Mitigative barriers come into play post-event, aiming to reduce impact. In the context of dropped objects, safety nets or protective barriers can shield workers below. Red Zones & No Go zones procedures minimize personnel exposure to potential harm. Additionally, emergency response plans and first aid measures offer immediate care, aiming to minimize injury severity.
Bow Tie Model’s Significance
The bow tie model’s strength lies in its encompassing approach. It maps the entire process, from causes to consequences, allowing industries to pinpoint risk management gaps and fortify measures.
In conclusion, the bow tie model presents a structured framework for navigating the risks tied to dropped objects. By pinpointing causes, establishing preventive barriers, gauging potential consequences, and setting up mitigative measures, industries can bolster workplace safety. This model’s visual nature also facilitates clear communication of risks and measures to all stakeholders, ensuring unified safety pursuits.







Share:
Related Blogs
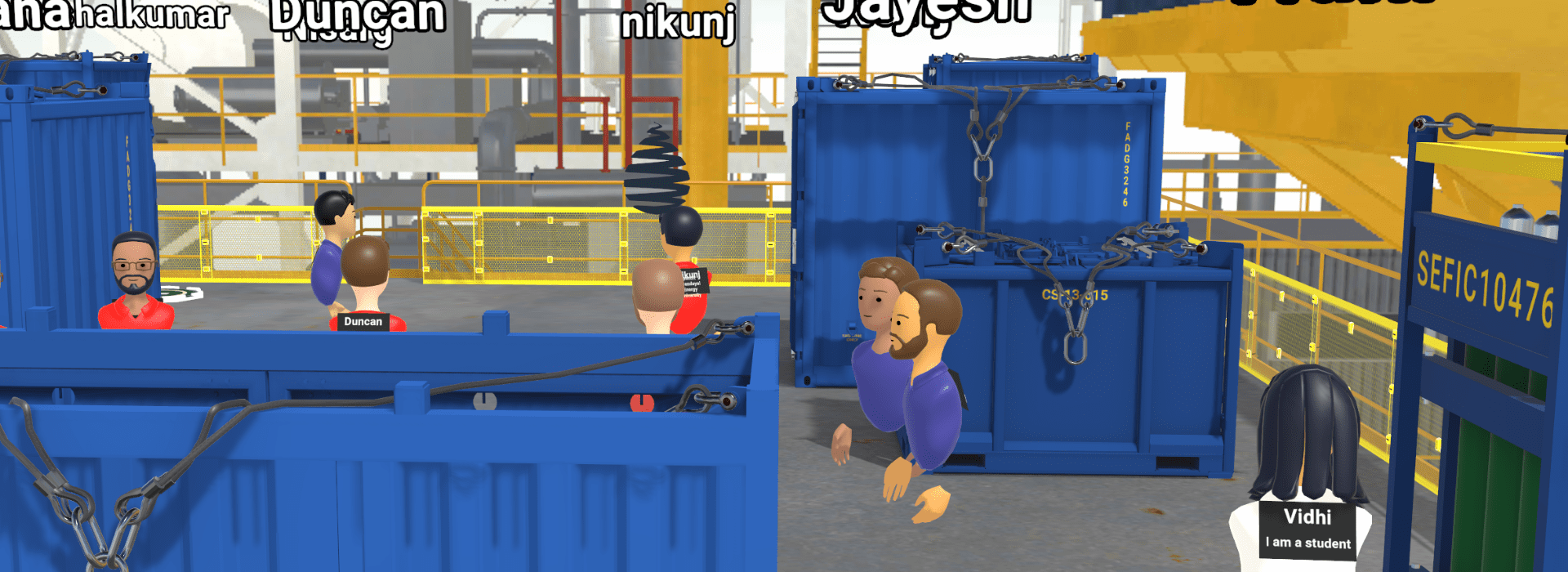
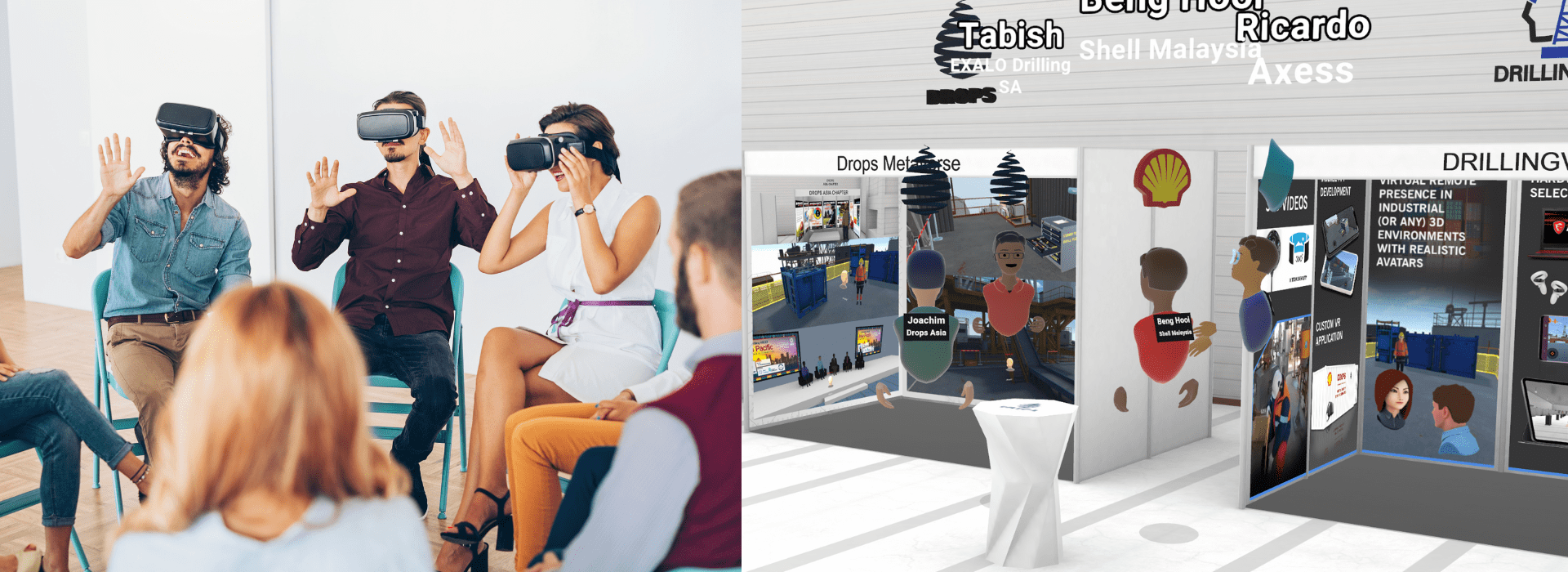
DROPS Metaverse VR Experience
DROPS Bow Tie
Galvanic Corrosion and DROPS